Symptoms of prostatitis depend on the form and cause of inflammation of the prostate gland, as well as the presence of the same disease. Symptoms often cross, which significantly complicates diagnosis.
Chronic prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis develops as an independent disease or as a complication of acute form of inflammation. During forgiveness, symptoms are weak or absent completely, with their severity becoming more clear. The clinical picture resembles acute prostatitis.
The first symptom of a chronic form of inflammation:
- Frequent urge to urinate;
- Silly pain in the lower abdomen;
- Discomfort in the prostate area (area from penis to anal) with long accommodation in sitting position. Next, sitting for more than an hour is impossible because of burning;
- Instant -over, painful urine;
- Boring pain in the rectum during water removal;
- Erection deterioration, discomfort in the thigh during ejaculation is possible.
The above signs in the form of chronic prostatitis are not indicated at once. Initially, this could be a lubricated orgasm, premature ejaculation, so a man should be pressed during urination, gradually joining.
In ultrasound with chronic inflammation, decreased prostate tissue density, increased level of reflection of fabric waves, observed. In place, it decreases with the presence of cysts or strengthens in the area of exposure to calcinates (stone), the focus of sclerosis (sealing from connective tissue, is formed by the process of recovery after acute inflammation). In the final stages of the focus of connective tissue and fibrosis, there are more. The size of the prostate gland is reduced. During visual diagnosis, it is difficult to distinguish it from the surrounding fiber.
Acute prostatitis
Acute forms of infectious prostatitis (bacteria) are characterized by rapid development. The severity of the symptoms depends on the degree of damage to the gland. With the form of catarrhal (inflammation only affects the channel), a man can feel a bit of discomfort during the pressure of the inguinal region. During iron finger examination, it increases and is almost painless.
Follicular (inflammation of the individual lobby of the gland), the parenchymal (inflammation of all prostate tissues) and abscesses (capsules with purulent content) are indicated by the overall symptom complex:

- Strong shooting pain in the thighs, giving rectum, penis, sacrum, in the internal hip, in the penis.
- Fever, general weakness. The active development of pathogens causes body intoxication with inflammation products.
- Removes when urinating, incomplete feeling of bladder (due to irritation of sphincters and uretral mucosa).
- Purulent release from the urethra (pus out of the prostate channel, open to the urethra).
- Sensation of severity in the perineum.
- A quick heart attack.
- Wormy urine with purulent yarn. Blood may appear.
With the form of parenchymal prostatitis, painful cramps and pulsating pain in the rectum make it difficult to get rid of urination. Small discharge occurs only in pose lying down with pressed feet. Often, prostate inflammation extends to the rectum, so the mucus begins to be extracted from the anus. The devotion to the background of the parenchymal form may stop completely due to severe edema from the gland.
External signs of acute prostatitis on ultrasound:
- Development of venous plexus. Vascular patterns are more clearly stated;
- Expansion of channels and gland capsules (swelling, uneven increases, contouring);
- Increased level of wave reflection with fabric;
- The seed bubbles on the prostate side are asymmetric due to heterogeneous filling, the channel that removes the seed is expanded.
With suspicious neoplasms, MRI or CT is set.
Stagnant prostatitis
The movement of prostatitis (it is also called bacteria without infection) can develop in young and older men. The main symptoms are similar to chronic chronic inflammation. A distinctive feature is that the discomfort of the urinary system is indicated and enhanced mainly due to long sexual abstinence. Extraction can cause sexual sexual intercourse, non -orgasm (sex without proper emotional color). Far, painful urine (wandering) is usually observed in the morning. However, if the previous day was a full orgasm, there was no cramps.
With this type, prostatitis is the amount of leukocytes in the secret of the gland not to exceed the norm, there is no pathogen flora in the third part of the urine.
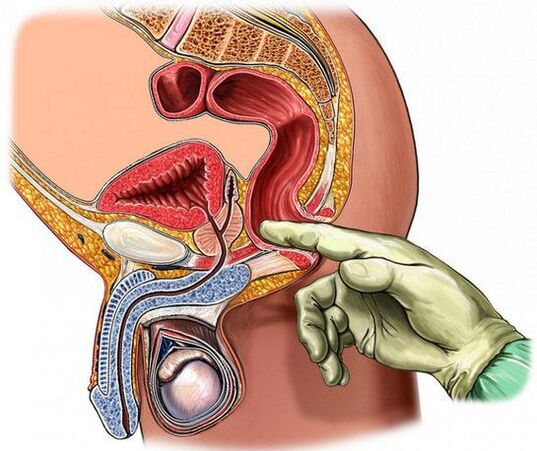
Calcular prostatitis
Calcular prostatitis has no specific symptoms. The presence of a stone in the gland does not mean the automatic development of its inflammation. With physical effort, background pain can be intensified. The migration of stones through the channel sometimes causes the appearance of blood in the urine.
During prostate ultrasound, calcinates are detected. Due to the increase in density, they are more effective in reflecting the waves emitted by the device.
Characteristics of manifestation of prostatitis at a young age and mature
Symptoms of various forms of prostatitis do not depend on the age category of a man. Young people are actively living a sexual life, so they often develop a form of infectious inflammation with corresponding signs.
Chronic prostatitis is diagnosed in men several years after the onset of sexual activity. Currently, due to the activity of hidden infections, the prostate structure is violated, the cellular immunity is reduced. Symptoms appear in time when pathological changes are irreversible.
Mature men are mainly experiencing urinary tract disorders, regular stupid pain in the perineum, and erectile disorders. Licking prostatitis at this age is worsened by the stagnant process in the pelvis against the background of androgenous failure and loss of muscle tone.
When and to whom to contact
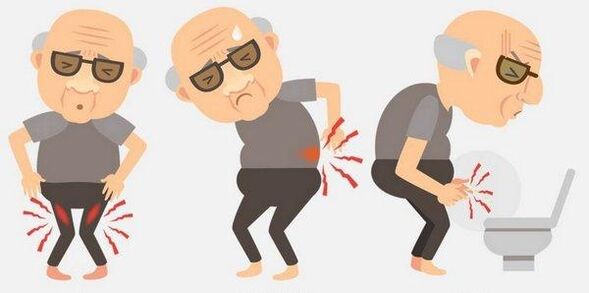
Any of the above symptoms are the reason for contacting a urologist or an andrologist (a diagnosis of prostatitis in clinical and home conditions). Many men avoid going to the doctor because of the negative attitude for prostate examination with the finger through the anus or trusie (ultrasound transmission). If the patient absolutely rejects this type of study, the doctor will offer transabdominal ultrasound - when the sensor leans on the lower stomach. The bladder should be filled (only 350 ml of fluid an hour before the procedure).
Based on ultrasound results, doctors determine the properties of prostate tissue wounds surrounding the tissues and bladder. To identify the cause of the inflammation, it is necessary to pass the urine, blood, prostatic secret (you need a rectal gland massage), in some cases and sperm.
What disease has the same symptoms
Many diseases have symptoms similar to prostatite. First of all, it is cystitis (bladder inflammation). It is characterized by frequent impulse to the toilet, destroying the lower abdomen, urine pain, muddy urine, sometimes with blood. Maybe a slight increase in temperature.
In men over 45, with symptoms of prostatitis, glands and gland cancer are mainly excluded. Inflammation of this pathological background is often a secondary sign. Symptoms of gland cancer are similar to the manifestation of chronic prostatitis: periodic urinary tract disorders in the thighs. Prostate is not painful with a finger study, but a compact node is found in its structure.
Far night urine, slow urine flow, incomplete bubble emptying feelings, leakage of drops from the urethra and weight in the perineum are characteristic of adenoma. The picture is explained by palpation and ultrasound: the prostate contour is preserved, the consistency is elastic, the surface is smooth, the iron is almost painless.
Urinary tract and pain in the thighs can occur with stones that are not infected with prostate - Calcinates are present, but around it there is no good environment to join the pathogen. The discomfort in the perineum in this case triggers physical activity, ejaculation. With the prostate feeling under the finger -Jari, creticing (stone crisis) can be felt, the gland body is dense, tuberous, moderate pain.
Urinary tract disorders, characteristics of chronic disease, are also characteristic of bladder sphincter sclerosis (obstruction across the urethra in the form of a cutting muscle). Pathology is often caused by prolonged prostate. In men under the age of 40, are rarely diagnosed.
For chronic prostatitis, expanded venous nodes (internal hemorrhoids) are often taken. They are available only using special diagnostic tools. Symptoms:
- Pain in the anus, gives to the sacrum and the throat;
- Erection violations;
- Strengthening pain in the rectum and perineum during water removal or prolonged discovery in sitting position.
The contour and consistency of the prostate has not changed. In its secret, pathological changes are not present.
Pain in the anus and perineum occurs with proxy - rectal inflammation. Features -Features are strong burning sensations in the anal during and after drainage, giving penis and throat. There is an impetus for urinary tract (every 20-30 minutes) followed by a urine. Prozatite often develops simultaneously with prostatitis. In this case, parallel therapy for both diseases is required.
Symptoms of prostatitis are also indicated by tuberculosis of the gland. In the risk zone of a man aged 20 to 40. In the early stages of development, the disease is almost symptomless. Sometimes, small pain in the rectum and perineum occurs. Urinary violation begins to the background of involvement in the pathological process of the gland, delivering a vessel that emits urine.
With tuberculosis, the purulent cavity forms in the prostate body. When they step in, the contents flow into the urethra and release from the penis during water removal. Bacteria that have fallen into the ureter irritate the mucous membranes, cause fast and painful urination. Through fiber, pus can spread to the rectum. In this case, there is an increase in temperature, weakness, sweating, weight loss.
Conclusion
The prostate gland through the nerve plexus is closely associated with other pelvic organs, inflammation that provides symptoms similar to prostatitis. Doctors must distinguish (distinguish) prostatitis from other diseases and identify related. Patients should not surprise the fact that with the symptoms of prostatitis, this examination is aimed not only on iron, but also to other organs, in particular, to the rectum. It is important to exclude their participation in the formation of pain and urinary tract disorders, otherwise treatment will be ineffective.